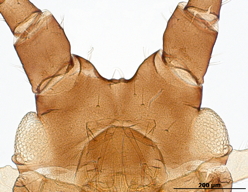
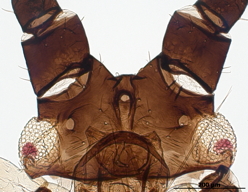
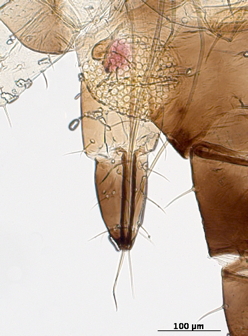
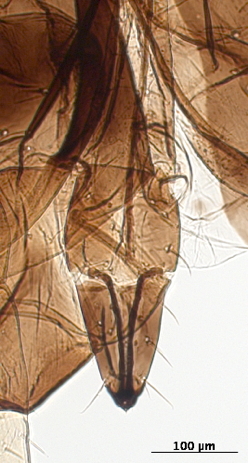
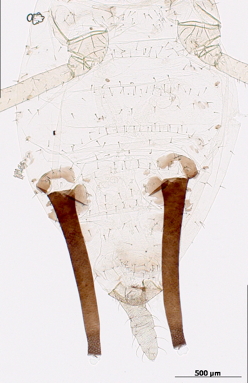
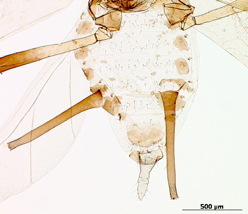
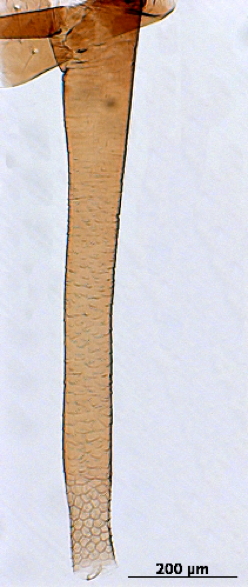
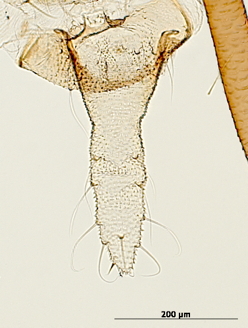
Macrosiphum rosae
feeds mostly on rosaceous plants.
Common names. Rose aphid.
Distribution. This aphid is globally distributed, except for eastern Asia.
Host associations. It feeds mostly on roseaceous plants, but it is known to feed on species in 15 other plant families.
Economic importance. It is particularly important on cultivated varieties and native species of Rosa, but also attacks a variety of ornamentals. It has been implicated in the transmission of at least 11 plant viruses.
See also. Taxonomy at Aphid Species File. Aphids on the World's Plants. Literature references.