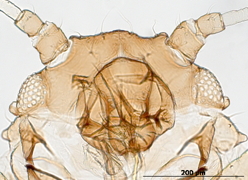
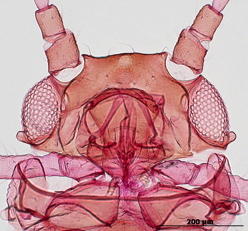
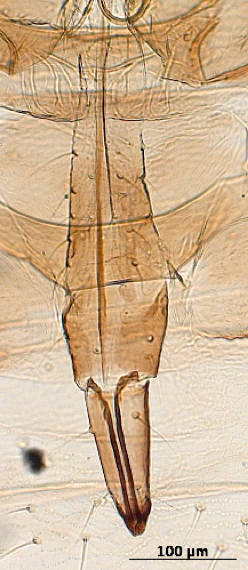
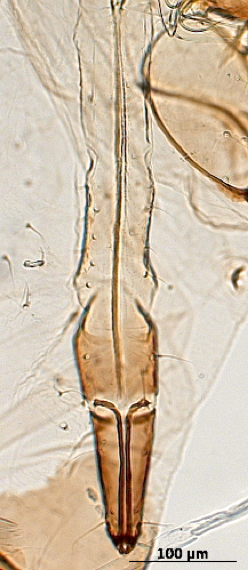
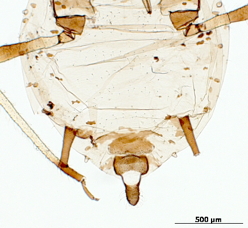
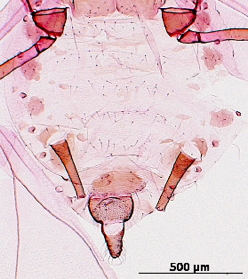
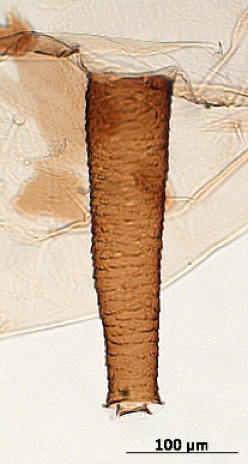
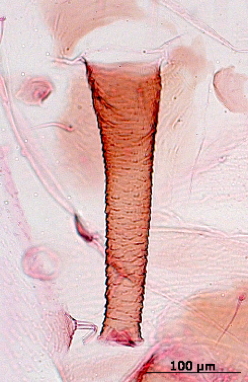
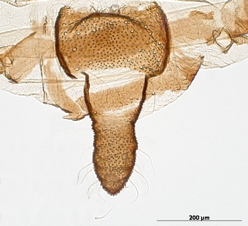
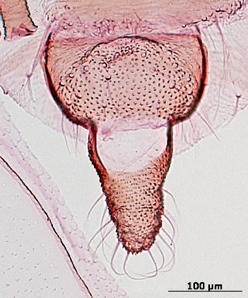
Aphis fabae
is one of the most polyphagous and widely distributed aphid species.
Common names. Bean aphid, Black bean aphid.
Distribution. This aphid is globally distributed, found commonly in temperate regions of the northern hemisphere and in cooler regions of South America, Africa, and the Middle East.
Host associations. It has one of the broadest host ranges, having been recorded from nearly 120 plant families.
Economic importance. It is particularly important on beans, peas, beets, crucifers, cucurbits, potato, tobacco, tomato, and tulip. Three recognized subspecies, in addition to the previously mentioned host plants, attack Arctium and Cirsium (Asteraceae), Euonymus (Celastraceae), Viburnum (Caprifoliaceae), Philadelphus (Hydrangeaceae), and Tropaeolum (Tropaeolaceae) and others. It has been implicated in the transmission of over 40 plant viruses.
See also. Taxonomy at Aphid Species File. Aphids on the World's Plants. Literature references.