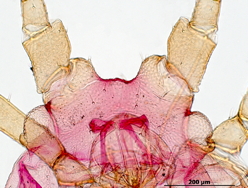
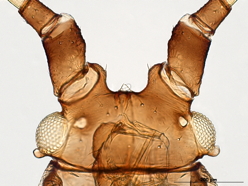
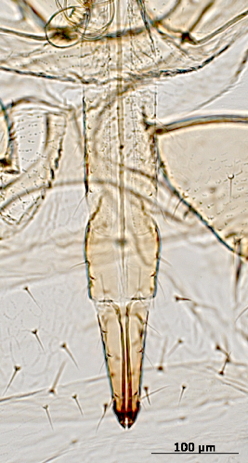
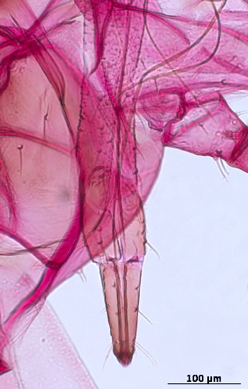
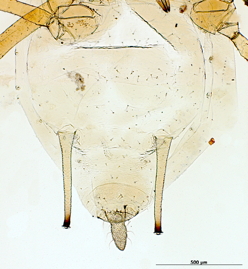
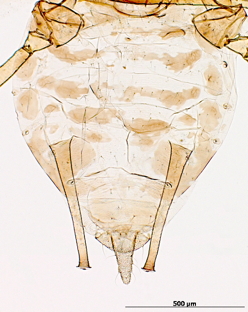
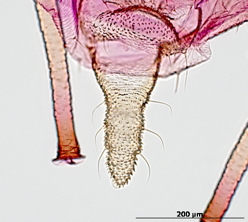
Aulacorthum solani
is one of the most polyphagous and widely distributed aphid species.
Common names. Foxglove aphid, Glasshouse-potato aphid.
Distribution. This aphid is globally distributed, located in all but the coldest terrestrial habitats.
Host associations. It has one of the broadest host ranges of any aphid, having been recorded from species of over 82 plant families, including monocots and dicots.
Economic importance. It is particularly important on tomato, peppers, and tobacco (Solanaceae), celery and carrots (Apiaceae), tulip bulbs (Lilaceae), cucurbits and legumes, but also attacks a broad range of other crops such as greenhouse strawberries and potato, and a variety of ornamentals. It has been implicated in the transmission of at lest 45 plant viruses.
See also. Taxonomy at Aphid Species File. Aphids on the World's Plants. Literature references.