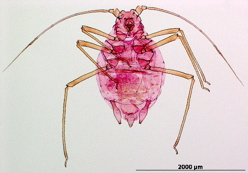
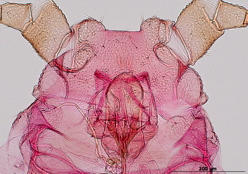
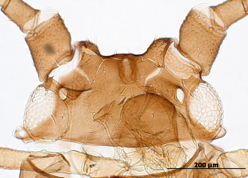
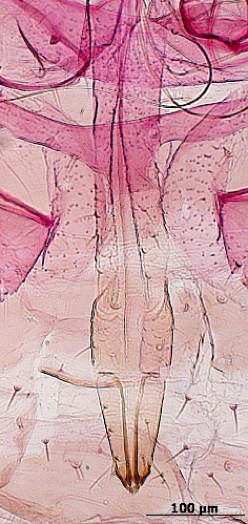
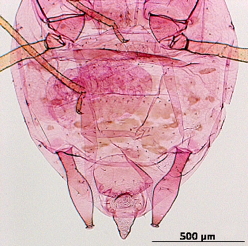
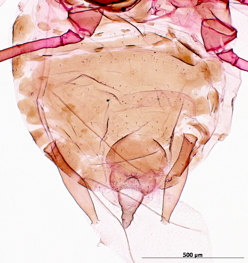
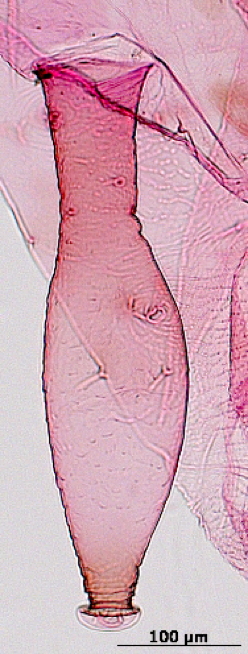
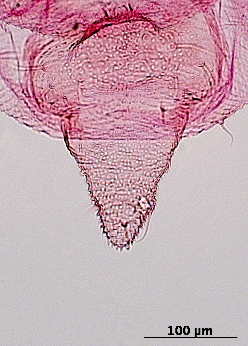
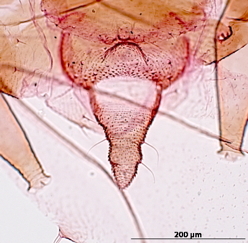
Rhopalosiphoninus staphyleae
is a globally distributed aphid species that feeds on lily and tulip.
Common names. Mangold aphid.
Distribution. This aphid is globally distributed, located in all but the coldest terrestrial habitats.
Host associations. It has been recorded from species of at least 16 plant families.
Economic importance. It is particularly important on lily and tulip (Liliaceae) and stored mangold beets (Chenopodiaceae) but also attacks a broad range of ornamentals. One subspecies is recognized, Rhopalosiphoninus staphyleae tulipaellus, and has been implicated in the transmission of at least 8 plant virus.
See also. Taxonomy at Aphid Species File. Aphids on the World's Plants. Literature references.