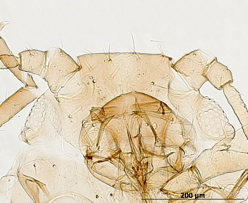
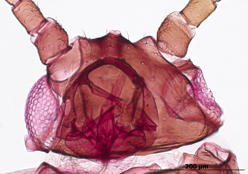
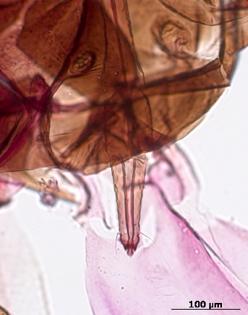
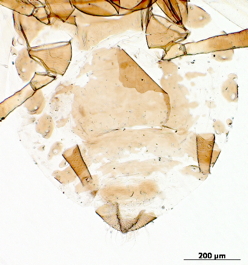
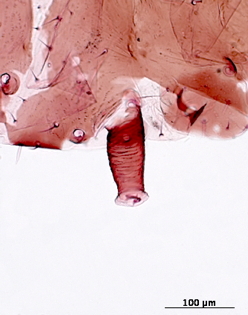
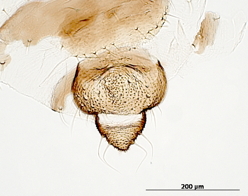
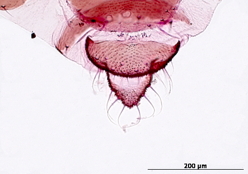
Dysaphis tulipae
a nearly cosmopolitan species that feeds mostly on monocot plant species.
Common names. Tulip bulb aphid.
Distribution. This aphid is globally distributed except for South America.
Host associations. It feeds mostly on monocots, having been recorded from species of at least 6 plant families.
Economic importance. It is particularly important on Lilium and Tulipa (Lilaceae), Crocus, Gladiolus, and Iris (Iridaceae), but also attacks Arum (Araceae), Musa (Musaceae), and various umbells. It has been implicated in the transmission of 2 plant viruses.
See also. Taxonomy at Aphid Species File. Aphids on the World's Plants.Literature references.
References
Blackman, R.L. and V.F. Eastop. 2000. Aphids on the World’s Crops, Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons with the Natural History Museum, London. x + 466 pages, 58 figures, 51 plates.
Blackman, R.L. and V.F. Eastop. 2006. Aphids on the World’s Herbaceous Plants and Shrubs. Volume 2 The Aphids. John Wiley & Sons with the Natural History Museum, London. viii + pages 1025-1439.
Chan, C.K., A.R. Forbes, and D.A. Raworth. 1991. Aphid-transmitted viruses and their vectors of the world. Agriculture Canada Technical Bulletin 1991-3E. 1-216 pp.
Holman, J. 2009. Host Plant Catalog of Aphids, Palaearctic Region. Springer Science and Business Media B.V. 1216 pp.